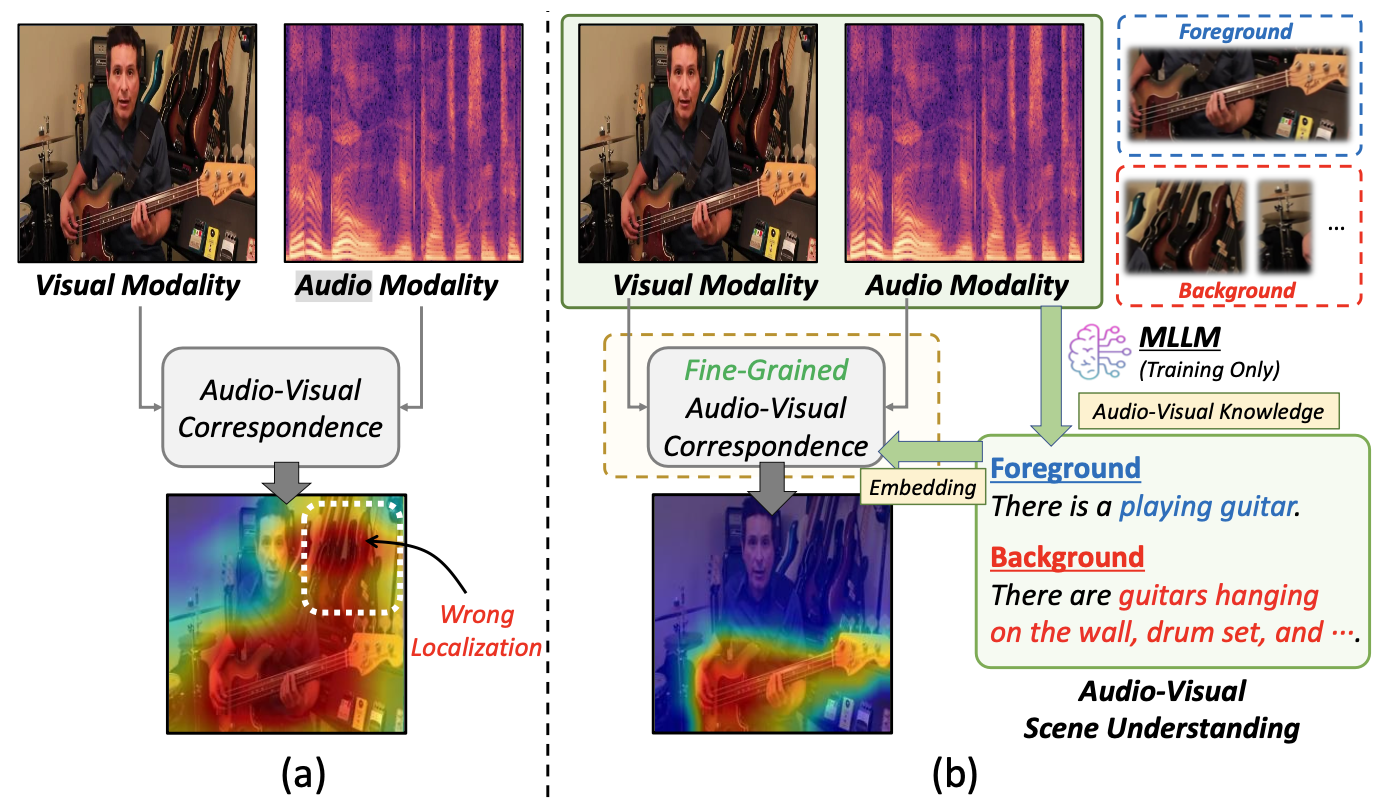
This work proposes a novel object-aware sound source localization framework that leverages Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to achieve fine-grained audio-visual correspondence. Unlike prior methods that rely mainly on simple feature alignment, we incorporate detailed scene understanding that distinguishes sound-making (foreground) and silent (background) objects. Specifically, MLLMs generate rich contextual descriptions of both audio and visual content, guiding the model to correctly identify actual sounding objects (e.g., a “playing” guitar) rather than visually similar but silent ones.
Two new losses boost performance:
- Object-aware Contrastive Alignment (OCA) Loss improves the model’s ability to differentiate sound-making from non-sounding objects.
- Object Region Isolation (ORI) Loss enforces clear spatial separation between distinct sound-emitting objects, preventing overlapping or confused localizations.
Extensive experiments on MUSIC, VGGSound, and variations (Solo/Duet/Trio) confirm that our method significantly enhances both single and multi-sound source localization in complex scenes. By fully leveraging audio-visual scene understanding, our approach achieves more accurate and robust localization in diverse real-world scenarios.
Links
- arXiv: (TBU)
- GitHub: (TBU)